Humidity Control
One of the ways to eliminate static electricity is humidity control.
You may have experienced static problems during winter when the air is dry, and in contrast, little or no static on rainy days. Static electricity and humidity are in fact closely correlated.
- Principle of static elimination through humidity control
- Example: Humidity control using a humidifier
Principle of static elimination through humidity control
High humidity means that there is a lot of moisture in the air. In such locations, your body contacts a large amount of small water droplets, making your skin moist. This is not limited to your skin, as this phenomenon also occurs for many other things.
- LOW HUMIDITY
-

Small amount of airborne moisture
- HIGH HUMIDITY
-
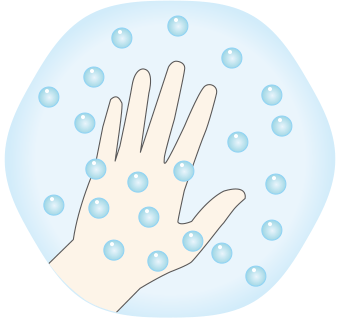
Large amount of airborne moisture
The surface of an object placed in a location with a lot of moisture in the air will contact a large amount of water droplets. Water conducts electricity, so a surface with lots of water on it conducts electricity easily.
If the object is grounded in this state, the static electricity will escape from the object. Also, a large amount of moisture in the air leads to static electricity naturally escaping along the airborne moisture. This means that humidity control is an effective way to create an environment where it is difficult for static electricity to accumulate.
- Objects and static electricity at high humidity
-
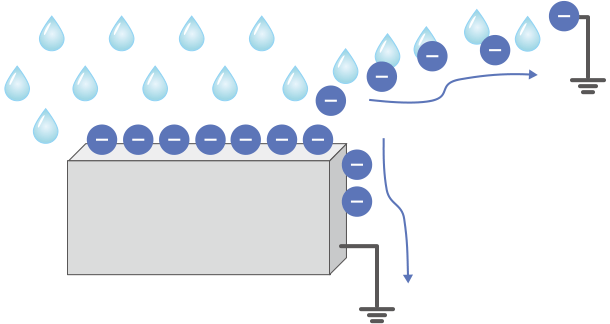
The static electricity accumulated in an object escapes along the water droplets on its surface or airborne moisture, finally returning to the Earth via ground.
The humidity makes it easier for the object to pass electricity, allowing its accumulated static electricity to escape via grounding.
- [Features]
- Makes it difficult for static electricity to accumulate
- [Precautions]
- Targets and devices may be negatively affected by condensation and rust.
It is difficult and expensive to control large areas under the same conditions.
Example: Humidity control using a humidifier
Humidifiers are commonly used for humidity control.
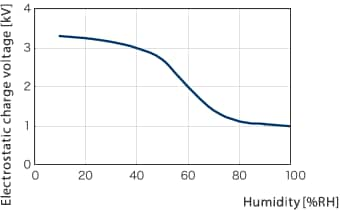
The graph on the right shows how static electricity is naturally discharged as humidity increases. As a guideline, static electricity is less likely to occur at relative humidity of more than 65%. Even if it does occur, it dissipates naturally at these relative humidities.
- [Effect]
- Suppresses the generation of static electricity and supports detailed tasks
- [Precautions]
- Machines and devices may be negatively affected by condensation and rust.